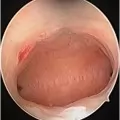
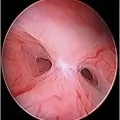
Hysteroscopic surgery is a procedure that allows a�doctor to look inside uterus in order to diagnose and treat causes of abnormal bleeding. Hysteroscopy is done using a hysteroscope, a thin, lighted tube that is inserted into the vagina to examine the cervix and inside of the uterus. Hysteroscopic surgery can be either diagnostic or operative.
Who are benefited by Hysteroscopic Surgery ?
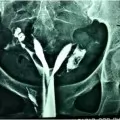
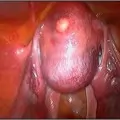
Some ladies have polyps or fibroids inside the uterine cavity which can only be removed through the cervical canal (i.e., not approachable Laparoscopically). Some have uterine septae (congenital partitions inside the uterine cavity). Both can cause Infertility and fibroids cause abnormal bleeding. Septated uteri� also cause recurrent miscarriages. Hysteroscopic resection of the septum produces dramatic results in these patients.
How are Hysteroscopic operations performed ?
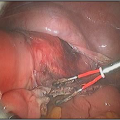
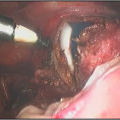
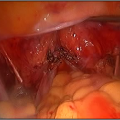
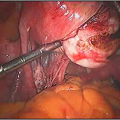
The hysteroscope allows good vision inside the uterus .The uterus is kept distended by a continuous flow of a liquid by� specialised pressure-controllong device. Specialised fine electrosurgical tools are passed into the cavity under vision and the pathology is tackled. The patient goes home the same day.
Hysteroscopy is useful in a number of uterine conditions:
- Asherman’s syndrome�(i.e. intrauterine adhesions). Hysteroscopic adhesiolysis is the technique of lysing adhesions in the uterus using either microscissors (recommended) or thermal energy modalities. Hysteroscopy can be used in conjunction with laparascopy or other methods to reduce the risk of perforation during the procedure.
- Endometrial polyp. Polypectomy.
- Gynecologic bleeding
- Endometrial ablation�(Some newer systems specifically developed for endometrial ablation such as the Novasure do not require hysteroscopy)
- Myomectomy�for�uterine fibroids.
- Congenital�uterine malformations�(also known as Mullerian malformations).
- Evacuation of retained products of conception�in selected cases.
- Removal of embedded�IUDs.
The use of hysteroscopy in�endometrial cancer�is not established as there is concern that cancer cells could be spread into the peritoneal cavity.
Hysteroscopy has the benefit of allowing direct visualization of the uterus, thereby avoiding or reducing iatrogenic trauma to delicate reproductive tissue which may result in�Asherman’s syndrome.
Hysteroscopy allows access to the�utero-tubal junction�for entry into the�Fallopian tube; this is useful for tubal occlusion procedures for�sterilization�and forfalloposcopy.